919. 完全二叉树插入器
题目描述:
完全二叉树 是每一层(除最后一层外)都是完全填充(即,节点数达到最大)的,并且所有的节点都尽可能地集中在左侧。
设计一种算法,将一个新节点插入到一个完整的二叉树中,并在插入后保持其完整。
实现 CBTInserter 类:
-
CBTInserter(TreeNode root) 使用头节点为 root 的给定树初始化该数据结构;
-
CBTInserter.insert(int v) 向树中插入一个值为 Node.val == val的新节点 TreeNode。使树保持完全二叉树的状态,并返回插入节点 TreeNode 的父节点的值;
-
CBTInserter.get_root() 将返回树的头节点。
测试用例:
示例 1:
输入 ["CBTInserter", "insert", "insert", "get_root"] [[[1, 2]], [3], [4], []]
输出 [null, 1, 2, [1, 2, 3, 4]]
解释 CBTInserter cBTInserter = new CBTInserter([1, 2]);
cBTInserter.insert(3); // 返回 1
cBTInserter.insert(4); // 返回 2
cBTInserter.get_root(); // 返回 [1, 2, 3, 4]
限制及提示:
- 树中节点数量范围为 [1, 1000]
- 0 <= Node.val <= 5000
- root 是完全二叉树
- 0 <= val <= 5000
- 每个测试用例最多调用 insert 和 get_root 操作 10^4 次
解题分析及思路:
本题可以采用层级遍历二叉树 🔗来解答。
本题一共三个方法,构造方法、插入方法、获取根节点方法。
获取根节点直接方法根节点即可,所以本题的重点在于怎么构建以及插入,而插入就决定了我们怎么去构建CBTInserter结构体,以及包含哪些变量。
而插入方法是将一个新节点插入到一个完整的二叉树中,仍然能够保持二叉树的完整,那么插入的值需要插入到第一个缺少子节点的节点上。
例如:
1
/
2
那么接下来的值就需要插入到1上,成为1的右节点。
1
/ \
2 3
而这种情况,就需要插入到2上,成为2的左节点。
那么怎么去记录这样的情况呢?
那么可以采用层级遍历的思想,将所有节点保存到队列中,每次插入新的值,取出第一个不完整的节点,成为该节点的子节点即可,而成为左节点还是右节点,在于左节点是否有值。
那么,结构体除了要包含根节点之外,还需要一个队列来保存其每一个节点。
type TreeNode struct {
Val int
Left *TreeNode
Right *TreeNode
}
type CBTInserter struct {
root *TreeNode
queue []*TreeNode
}
初始化时,将所有的节点都保存到队列当中,方便后续插入便利。
这里用了另一个队列来层级遍历这棵树,当然,如果不嫌麻烦的话,可以用下标去获取。
func Constructor(root *TreeNode) CBTInserter {
queue := make([]*TreeNode, 0)
tempQueue := []*TreeNode{root}
for len(tempQueue) > 0 {
node := tempQueue[0]
tempQueue = tempQueue[1:]
queue = append(queue, node)
if node.Left != nil {
tempQueue = append(tempQueue, node.Left)
}
if node.Right != nil {
tempQueue = append(tempQueue, node.Right)
}
}
return CBTInserter{
root,
queue,
}
}
在执行插入的时候,遍历队列,直到找到第一个不完整的节点,并且将val赋值到该节点上,并且同时将val的这个节点你保存到队列中。
func (this *CBTInserter) Insert(val int) int {
node := this.queue[0]
if node.Left != nil && node.Right != nil {
this.queue = this.queue[1:]
return this.Insert(val)
}
child := &TreeNode{
Val: val,
}
if node.Left == nil {
node.Left = child
} else if node.Right == nil {
node.Right = child
this.queue = this.queue[1:]
}
this.queue = append(this.queue, child)
return node.Val
}
优化:可以只将不完整的节点push到队列中
复杂度:
- 时间复杂度:O(n)
- 空间复杂度:O(n)
执行结果:
- 执行用时:4 ms, 在所有 Go 提交中击败了94.59%的用户
- 内存消耗:6.6 MB, 在所有 Go 提交中击败了35.14%的用户
Tags :
通过次数 36.4K 提交次数 54K 通过率 67.4%

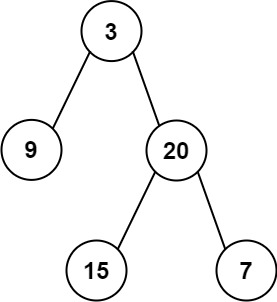 ```
输入: preorder = [3,9,20,15,7], inorder = [
```
输入: preorder = [3,9,20,15,7], inorder = [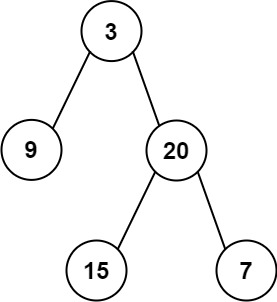 ```
输入:inorder = [9,3,15,20,7], postorder
```
输入:inorder = [9,3,15,20,7], postorder 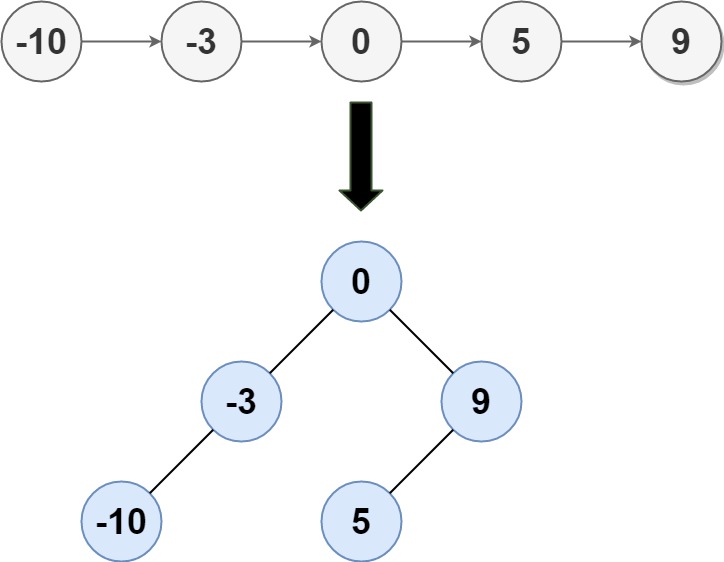 ```
输入: head = [-10,-3,0,5,9]
输出: [0,-3,9
```
输入: head = [-10,-3,0,5,9]
输出: [0,-3,9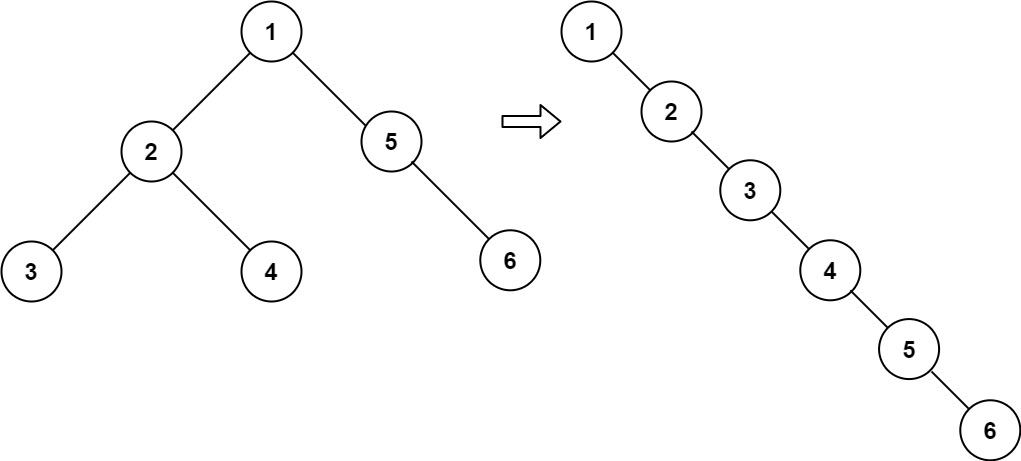 ```
输入:root
```
输入:root