784. 字母大小写全排列
题目描述:
给定一个字符串 s ,通过将字符串 s 中的每个字母转变大小写,我们可以获得一个新的字符串。
返回 所有可能得到的字符串集合 。以 任意顺序 返回输出。
示例 1:
输入:s = "a1b2"
输出:["a1b2", "a1B2", "A1b2", "A1B2"]
示例 2:
输入: s = "3z4"
输出: ["3z4","3Z4"]
提示:
1 <= s.length <= 12s由小写英文字母、大写英文字母和数字组成
解题分析及思路:
方法:深度优先遍历
思路:
由于数据量不大的原因,这里可以直接采用深度优先遍历的方法从前往后针对每个字母进行分析
当下标为index时,此时s[index]有两种情况:
s[index]为数字时,直接保留s[index]为字母时,采取两种方法:保留、大小写转换
所以针对dfs方法:
- 终止条件为 下标 达到 s 的长度
- 访问下标index,针对两种情况进行处理
- 访问下标index结束,index++ 继续访问,直到终止
import "unicode"
func letterCasePermutation(s string) []string {
result := make([]string, 0)
dfs([]rune(s), 0, len(s), &result)
return result
}
func dfs(s []rune, index int, l int, result *[]string) {
if index == l {
*result = append(*result, string(s))
return
}
dfs(s, index+1, l, result)
if unicode.IsLetter(s[index]) {
s[index] = s[index] ^ 32
dfs(s, index+1, l, result)
}
}
复杂度:
- 时间复杂度:O(n * 2n)
- 空间复杂度:O(1)
执行结果:
- 执行耗时:5 ms,击败了80.81% 的Go用户
- 内存消耗:6.2 MB,击败了40.40% 的Go用户
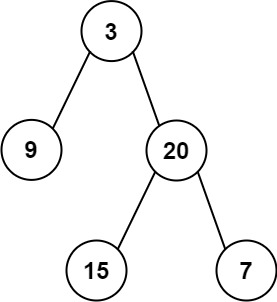 ```
输入: preorder = [3,9,20,15,7], inorder = [
```
输入: preorder = [3,9,20,15,7], inorder = [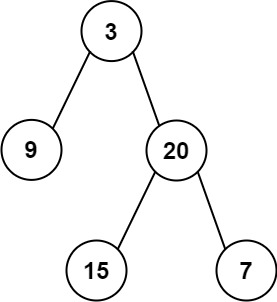 ```
输入:inorder = [9,3,15,20,7], postorder
```
输入:inorder = [9,3,15,20,7], postorder 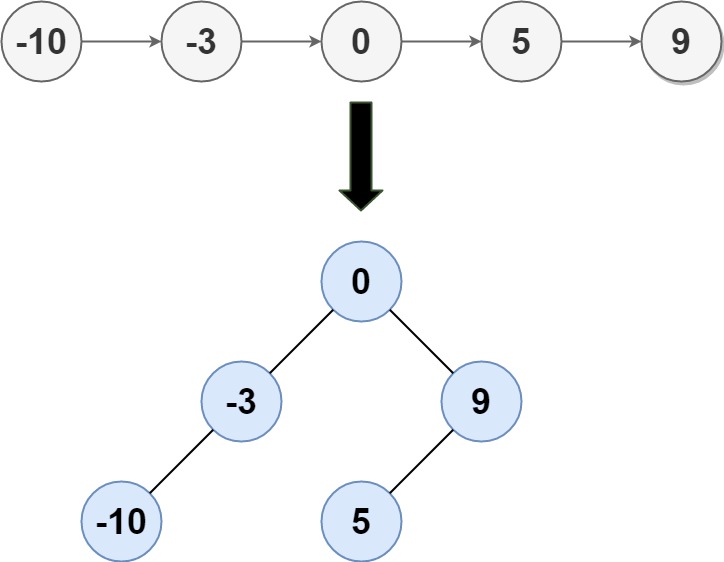 ```
输入: head = [-10,-3,0,5,9]
输出: [0,-3,9
```
输入: head = [-10,-3,0,5,9]
输出: [0,-3,9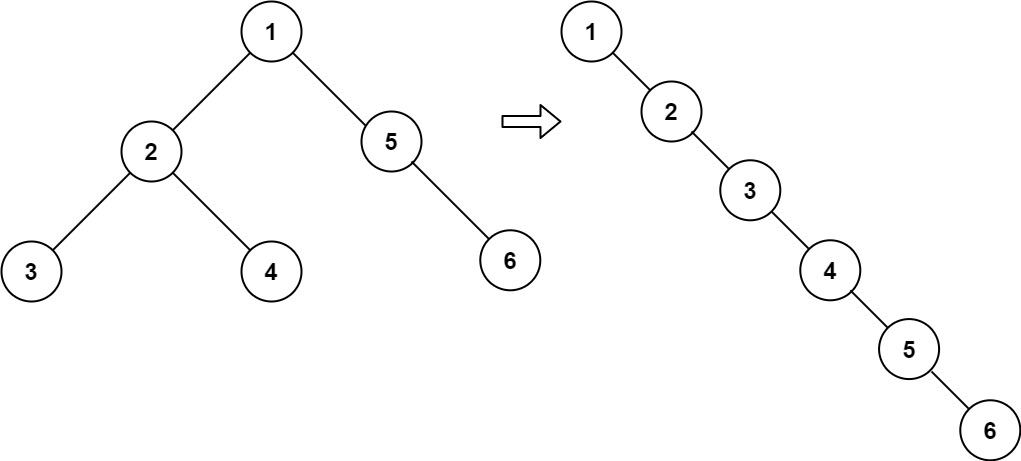 ```
输入:root
```
输入:root