225. 用队列实现栈
题目描述:
请你仅使用两个队列实现一个后入先出(LIFO)的栈,并支持普通栈的全部四种操作(push、top、pop 和 empty)。
实现 MyStack 类:
- void push(int x) 将元素 x 压入栈顶。
- int pop() 移除并返回栈顶元素。
- int top() 返回栈顶元素。
- boolean empty() 如果栈是空的,返回 true ;否则,返回 false 。
注意:
- 你只能使用队列的基本操作 —— 也就是 push to back、peek/pop from front、size 和 is empty 这些操作。
- 你所使用的语言也许不支持队列。 你可以使用 list (列表)或者 deque(双端队列)来模拟一个队列 , 只要是标准的队列操作即可。
示例 1:
输入:
["MyStack", "push", "push", "top", "pop", "empty"]
[[], [1], [2], [], [], []]
输出:
[null, null, null, 2, 2, false]
解释:
MyStack myStack = new MyStack();
myStack.push(1);
myStack.push(2);
myStack.top(); // 返回 2
myStack.pop(); // 返回 2
myStack.empty(); // 返回 False
提示:
- 1 <= x <= 9
- 最多调用100 次 push、pop、top 和 empty
- 每次调用 pop 和 top 都保证栈不为空
解题分析及思路:
思路:
由于Go中没有高级数据结构,所以我们可以使用切片来模拟栈的操作。
type MyStack struct {
stack []int
}
func Constructor() MyStack {
return MyStack{make([]int, 0)}
}
func (this *MyStack) Push(x int) {
this.stack = append(this.stack, x)
}
func (this *MyStack) Pop() int {
pop := this.stack[len(this.stack)-1]
this.stack = this.stack[:len(this.stack)-1]
return pop
}
func (this *MyStack) Top() int {
return this.stack[len(this.stack)-1]
}
func (this *MyStack) Empty() bool {
return len(this.stack) == 0
}
但是很显然,这种方法并不是题目要求的方法。我们可以使用一个队列来模拟栈的操作。
若使用队列操作模拟栈的操作,我们可以使用两种方法:
- 入栈时,将元素入队列,然后将队列中的元素依次出队列,再入队列,这样就可以实现栈的后进先出的特性。
- 出栈时,将队列中的元素依次出队列,再入队列,直到队列中只剩下一个元素,这个元素就是栈顶元素。
type MyStack struct {
queue []int
}
func Constructor() MyStack {
return MyStack{make([]int, 0)}
}
func (this *MyStack) Push(x int) {
queue := []int{x}
for index := range this.queue {
queue = append(queue, this.queue[index])
}
this.queue = queue
}
func (this *MyStack) Pop() int {
pop := this.queue[0]
this.queue = this.queue[1:]
return pop
}
func (this *MyStack) Top() int {
return this.queue[0]
}
func (this *MyStack) Empty() bool {
return len(this.queue) == 0
}
复杂度:
- 时间复杂度:O(N)
- 空间复杂度:O(1)
执行结果:
- 执行耗时:0 ms,击败了100.00% 的Go用户
- 内存消耗:1.8 MB,击败了75.48% 的Go用户
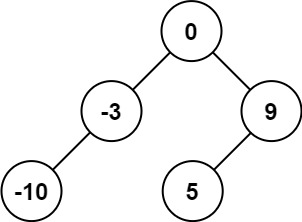 ```
输入:nums = [-10,-3,0,5,9]
输出:
```
输入:nums = [-10,-3,0,5,9]
输出: